Exploring Keto-Friendly Fruits for Your Diet


Intro
As the ketogenic diet continues to gain popularity, many individuals wonder about the feasibility of including fruits in such a low-carb regimen. Fruits are traditionally considered a healthy food group, but they can be high in sugars and carbohydrates. This article aims to clarify which fruits can be enjoyed while adhering to a keto diet. Understanding the carbohydrate content and glycemic index of fruits is essential. Through this exploration, we will provide valuable insights into the nutritional benefits of certain fruits, helping to bridge the gap between keto restrictions and healthy eating habits.
Key Takeaways
- The ketogenic diet places a strong emphasis on reducing carbohydrate intake.
- Not all fruits fit within the carb limits of a keto diet, yet certain ones are more suitable.
- Some keto-friendly fruits include berries, avocados, and olives due to their lower sugar content.
- The glycemic index of a fruit can play a crucial role in its compatibility with a low-carb lifestyle.
"Understanding the balance between healthy fruits and a ketogenic diet is crucial for both enjoyment and adherence."
Nutritional Benefits of Keto-Friendly Fruits
When selecting fruits for a ketogenic diet, opting for those that are lower in carbohydrates is critical.
- Berries (strawberries, raspberries, blueberries): These small fruits are low in sugar and packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber.
- Avocado: This fruit is unique due to its high-fat content, providing healthy monounsaturated fats along with fiber and potassium.
- Olives: Rich in healthy fats and low in carbohydrates, olives are ideal for snacking on a keto plan.
The nutritional benefits of these options extend beyond just carbohydrate content. They offer essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health, making them an excellent addition to any diet.
Practical Tips
Incorporating Fruits in a Keto Diet
Incorporating fruits into a ketogenic diet does not have to be daunting. Here are some practical steps:
- Mind Portions: Keep track of the serving sizes to avoid exceeding carb limits.
- Choose Wisely: Focus on low-carb fruits mentioned above.
- Pairing: Combine fruits with high-fat foods, such as nuts or cheese to further balance macro-nutrient intake.
Suggested Routines
- Meal Planning: Plan meals to include keto-friendly fruits. This can decrease impulse eating of non-keto items.
- Glycemic Monitoring: Use a glucometer to understand how different fruits affect your blood sugar levels.
By following these strategies, integrating keto-friendly fruits into your diet can enhance both variety and nutrition, ensuring that you stay within your dietary goals without sacrificing flavor or enjoyment.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet has gained significant popularity in recent years. The method emphasizes drastically reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing fats. This approach can lead to a metabolic state called ketosis, where the body relies primarily on fat for energy.
Understanding the ketogenic diet is crucial for anyone looking to incorporate fruits into their meal plans effectively. Knowledge of how the body processes different macronutrients can influence food choices. Also, awareness of the benefits and challenges helps in navigating dietary restrictions and achieving personal health goals.
Definition of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as "keto," is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet. Its origin can be traced back to the early 20th century, initially used to treat epilepsy. The standard micro nutritional breakdown is typically around 70-75% fats, 20-25% protein, and 5-10% carbohydrates.
This unique composition alters the body's typical energy mechanism. Instead of glucose from carbs, the body begins to convert fats into ketones which become the primary source of energy. The result is a shift in how one experiences hunger, energy levels, and even mood.
Key Principles of Keto
The primary principles of the ketogenic diet include:
- Low Carbohydrate Intake: Reducing daily carb intake is essential to enter and maintain ketosis.
- High Fat Consumption: Emphasizing healthy fats is crucial. Sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil are often included.
- Moderate Protein: Unlike many diets, keto does not prioritize protein. Instead, it aims for a balanced intake to maintain muscle mass without disrupting ketosis.
Moreover, these guidelines underscore the importance of choosing the right types of food. Adhering to these principles is vital for those exploring the compatibility of keto with fruits.
Role of Carbohydrates in Keto
Carbohydrates play a complex role in the ketogenic diet. Generally, on a standard diet, carbs are the body's primary energy source. However, during ketogenic conditions, the goal is to minimize their availability.
By restricting carbs, the body adapts by burning fat for fuel instead. This metabolic adaptation takes some time, usually a few days. Upon adaptation, many individuals report increased energy and sustained satiety.
Awareness of carbohydrate content in foods, especially fruits, becomes essential. While fruits are often seen as healthy, many contain high levels of sugars and carbs. Hence, understanding which fruits align with the ketogenic framework aids in making informed dietary choices.


Fruits and Their Role in Diets
Fruits play a complex role in diets, including in the context of the ketogenic diet. Understanding their place involves diving into the nutritional profiles and inherent benefits they offer. Numerous fruits offer vital vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them an important component of a balanced diet. However, for those pursuing keto, the focus shifts to carbohydrate content and how different fruits can fit into a low-carb approach.
It's essential to note that while many fruits are high in vitamins, their carbohydrate counts can vary significantly. Incorporating the right fruits into a ketogenic lifestyle requires an understanding of their nutritional values, potential health benefits, and common misconceptions.
Nutritional Value of Fruits
Fruits contain a variety of essential nutrients. They are often rich in vitamins such as vitamin C, folate, and potassium. Each type of fruit has a different profile of micronutrients. For example, citrus fruits like oranges are particularly high in vitamin C, while bananas provide potassium. Nevertheless, fruits also carry carbohydrates in the form of natural sugars, which can become a concern when following strict keto guidelines.
To quantify, here are a few examples of keto-friendly fruits and their carb content:
- Raspberries: Approximately 5 grams of net carbs per 100 grams.
- Blackberries: About 4.9 grams of net carbs per 100 grams.
- Avocado: Roughly 2 grams of net carbs per 100 grams.
This indicates a relatively low carbohydrate content compared to other fruits, making them more suitable for a ketogenic diet.
Health Benefits of Fruits
Incorporating fruits into your diet has numerous health benefits, including promoting digestive health, enhancing immune function, and providing antioxidants. Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress in the body, which can lead to inflammation and other diseases. Moreover, many fruits have a high fiber content, aiding in digestion and contributing to a feeling of fullness. This can be particularly useful for those on a ketogenic diet who may struggle with hunger when reducing carbohydrate intake.
"In moderation, keto-friendly fruits can complement a low-carb diet while still supporting overall health."
However, it is crucial to focus on the portions and types of fruits chosen. Excess carbohydrates from high-sugar fruits can quickly lead a person to exceed their daily carb allowance.
Common Myths About Fruits
Several myths surround fruits, especially regarding their fit within a ketogenic framework. One prevalent myth is that all fruits are unhealthy or to be avoided on keto. This view oversimplifies the topic and fails to recognize the diversity among fruits.
Another misconception is that natural sugars in fruits are the same as refined sugars. Natural sugars, when consumed along with the fiber, vitamins, and minerals found in whole fruits, do not impact blood sugar in the same way as processed sugars.
Additionally, it's often believed that fruit consumption must be entirely avoided for weight loss. In actuality, when selected wisely and consumed in appropriate portions, some fruits can provide nutritional benefits without derailing dietary ambitions.
Keto-Friendly Fruits
Understanding which fruits fit well within a ketogenic diet is critical for individuals looking to maintain low carbohydrate intake while still enjoying the natural sweetness and nutritional benefits of fruits. The importance of this topic lies in identifying the right options that can support health without exceeding the carb limits typically prescribed in a keto regimen. Each of the fruits discussed in this section offers unique advantages that can enhance one's nutrient profile while being compatible with the ketogenic diet.
Berries
Berries are among the most recommended fruits for people following a ketogenic lifestyle. Their low carbohydrate content and high fiber levels make them an excellent option for satisfying sweet cravings without significantly impacting blood sugar levels.
Raspberries
Raspberries stand out due to their exceptional low carbohydrate content, with about 5.5 grams of net carbs per 100 grams. This makes them a favorable choice for those monitoring their carb intake. The high fiber content of raspberries can aid in digestion. Moreover, they are rich in antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which provide various health benefits, including supporting heart health. The unique feature of raspberries is their balance of sweetness and tartness, making them versatile in both sweet and savory dishes.
Blackberries
Blackberries also offer low carbohydrate counts, aligning well with keto guidelines. With approximately 4.9 grams of net carbs per 100 grams, they can be easily integrated into meals or eaten on their own. Their key characteristic is the richness in vitamins such as vitamin C and K, which play roles in immunity and bone health. The advantage of blackberries is their high water content, which contributes to hydration while providing essential nutrients, making them a healthy addition to a keto diet.
Strawberries
Strawberries are another keto-friendly fruit, with about 7.7 grams of net carbs per 100 grams. They are popular for their flavor and versatility. Strawberries contain high levels of vitamin C, which can enhance skin health and boost the immune system. One unique feature is their ability to satisfy sweet cravings while still aligning with low-carb principles. However, it is important to consume them in moderation, as the carb content, while reasonable, is still higher than some other berries.
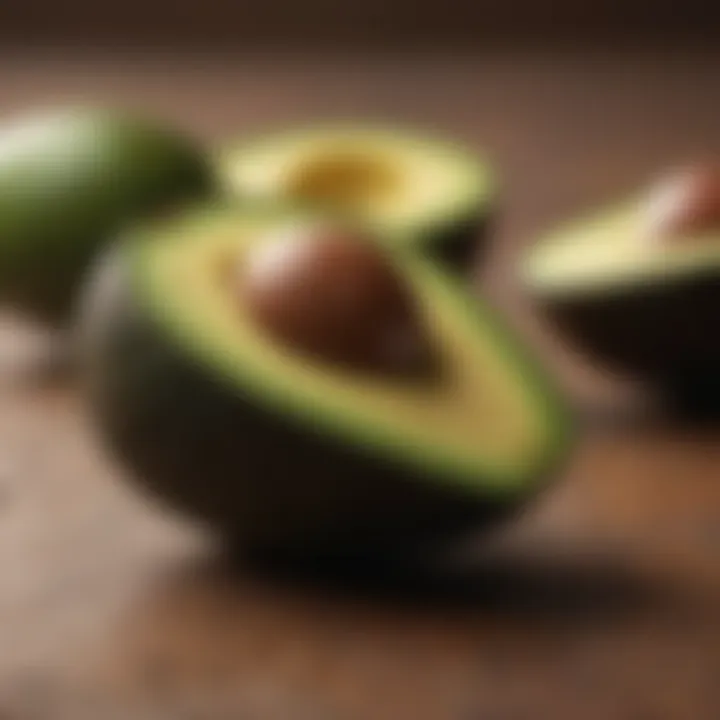
Avocado
Avocado is often touted as one of the best fruits for a ketogenic diet. Unlike most fruits, it is low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats, specifically monounsaturated fats. A typical avocado contains about 2 grams of net carbs per 100 grams, making it extremely suitable for maintaining ketosis. The beneficial aspect of avocados is their high fiber content, which aids in digestion. Furthermore, avocados provide a range of nutrients, including potassium, which is important for heart health and regulating blood pressure. Their creamy texture makes them a delightful addition to salads and smoothies, also providing a feeling of fullness.
Olives
Olives deserve mention due to their impressive fat content and minimal carbohydrates. With approximately 3 grams of net carbs per 100 grams, they are a practical choice for keto dieters looking for snacks or a flavorful addition to meals. The high amount of healthy fats in olives, particularly oleic acid, promotes heart health and can also help improve cholesterol levels. Adding olives to salads or as part of a charcuterie board can offer a satisfying and nutritious option.


Coconut
Coconut, especially in the form of coconut oil or unsweetened coconut flakes, fits seamlessly into the ketogenic lifestyle. The carb content in coconut meat is relatively low, generally around 6 grams of net carbs per 100 grams. Besides being low in carbs, coconuts are rich in medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are known for providing quick energy and may support weight loss. It is a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes, enhancing flavor while contributing to healthy fat intake.
Lemons and Limes
Citrus fruits like lemons and limes are also keto-friendly. They contain very low levels of carbohydrates, about 6-7 grams of net carbs per fruit. These fruits are primarily used for their juice and zest, adding flavor without significantly impacting carbohydrate counts. Lemons and limes are high in vitamin C and can improve the absorption of nutrients from other foods. Their unique feature is their ability to elevate the flavors in savory dishes and beverages, making them an ideal choice for enhancing overall meals without added carbs.
Fruits to Avoid on Keto
As scientifically inclined individuals, it is crucial to understand the implications of fruit consumption in the context of a ketogenic diet. While fruits can offer various health benefits, certain types can disrupt the delicate balance required for maintaining ketosis. Excessive carbohydrate intake, particularly from fruits that are high in sugars, can lead to a halt in fat-burning processes that the Keto diet aims to optimize. Therefore, a comprehensive grasp of which fruits should be avoided helps individuals make informed decisions that align with their dietary goals.
High-Carbohydrate Fruits
High-carbohydrate fruits are primarily those that contain a significant amount of sugars and carbohydrates, making them unsuitable for a ketogenic diet. Common examples include bananas, grapes, and apples. Each of these fruits carries varying levels of sugar that can quickly accumulate under a low-carb dietary model.
- Bananas: One medium banana contains around 27 grams of carbohydrates.
- Grapes: One cup of grapes provides approximately 27 grams as well.
- Apples: A medium apple has about 25 grams of carbohydrates.
These carbohydrate counts can easily exceed the daily limit for individuals on a strict Keto diet. Hence, it is essential to recognize the carbohydrate content in these fruits and consider alternatives that are lower in sugar.
Dried Fruits
Dried fruits pose a unique challenge for those adhering to a ketogenic lifestyle. While they may appear to be a healthy option, the dehydration process concentrates the sugars present, resulting in high carbohydrate content. Examples such as raisins, apricots, and dates are often deceptively calorie-dense. A small serving can yield a high level of carbohydrates that is difficult to manage within keto parameters.
- Raisins: Just one ounce packs roughly 22 grams of carbohydrates.
- Dried Apricots: An ounce of dried apricots has about 21 grams.
- Dates: A single Medjool date contains about 16 grams of carbohydrates.
It is vital for practitioners and patients alike to maintain vigilance concerning dried fruits, as they can easily disrupt the state of ketosis due to their concentrated sugar levels.
Tropical Fruits
Tropical fruits are often celebrated for their vibrant flavors and nutritional value, but they typically harbor a load of carbohydrates, making them incompatible with a ketogenic diet. Fruits like mangoes, pineapples, and papayas should be avoided or consumed minimally, as they can pose substantial risks to maintaining ketosis.
- Mangoes: One medium mango averages about 50 grams of carbohydrates.
- Pineapples: A cup of pineapple chunks can add around 22 grams to your carb count.
- Papayas: A serving of papaya provides approximately 15 grams of carbohydrates.
These examples illustrate the need for careful consideration when consuming fruits typically categorized as healthy. To achieve optimal results on a ketogenic diet, it may be more beneficial to prioritize fruits lower in sugars while being mindful of overall carbohydrate intake.
Carbohydrate Counting with Fruits
Carbohydrate counting is a crucial component of following a ketogenic diet. Understanding how different fruits fit into your carbohydrate allowance can help you maintain ketosis, which is the metabolic state aimed for in keto. With fruits often perceived as healthy, it can be easy to forget that some can contribute significantly to your carb intake. In this section, we will look at specific elements surrounding carbohydrate counting, its benefits, and important considerations.
One key benefit of carbohydrate counting is that it provides clarity on what you eat. This precision allows individuals to manage their daily carb intake, thus making it easier to stay within the desired limits for optimal ketosis. Additionally, understanding carbohydrate content empowers one to choose low-carb fruits over those that can spike insulin levels.
When counting carbs, it is essential to have an awareness of the fruit’s fiber content. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body does not digest. Therefore, the concept of net carbs emerges, which is crucial for keto dieters. The net carb count is found by subtracting the grams of fiber from the total carbohydrates.
This process ensures that individuals are informed and strategic in their fruit consumption. It helps in selecting fruits that align with the goal of minimizing carb intake while still allowing for the enjoyment of some fruit flavors.
"Carbohydrate counting makes managing a keto lifestyle more feasible and enjoyable."
Furthermore, one should consider not just the amount of fruit consumed, but also the frequency. Achieving a balance is vital. Eating small amounts of fruit occasionally might fit within the daily carb allowance, while frequent or large servings may lead to exceeding dietary goals. \n Overall, being diligent about carbohydrate counting in relation to fruits can be beneficial for ensuing adherence to a ketogenic diet and achieving health goals.
Understanding Net Carbs
Net carbs play a significant role in a ketogenic diet. The calculation involves subtracting dietary fiber and certain sugar alcohols from total carbs to find out the carbohydrates that affect blood sugar levels. Since fiber is not digested, it does not contribute to insulin spikes or a rise in blood glucose. For example, if a fruit contains 10 grams of total carbohydrates and 5 grams of fiber, the net carbs would be 5 grams.
Net carbs help dieters focus on the carbohydrates that truly impact their diet. This approach is particularly useful when selecting fruits, as some fruits might appear high in carbs but could be low in net carbs due to fiber content.
Portion Control
Portion control is vital when incorporating fruits into a keto diet. Even the more favorable fruits can lead to high carbohydrate intake if consumed in large amounts. Measuring or estimating portions can help maintain balance. This practice may include using a food scale or app to track intake and ensure moderation.

One effective way to manage this is by integrating fruits into meals or snacks thoughtfully. For instance, adding a small serving of berries to a dish allows for flavor enhancement without substantial carb overload.
Incorporating Fruits into a Keto Diet
Incorporating fruits into a ketogenic diet presents an opportunity for variety and essential nutrients. Understanding how to integrate fruits while maintaining a low carbohydrate intake is crucial for anyone following this particular eating plan. Proper incorporation of fruits can enhance the diet’s flavor and nutritional profile, helping adherents meet their macro requirements without compromising their goals.
When discussing fruits in the context of a keto diet, it’s important to focus on a few specific elements. First, not all fruits carry the same carbohydrate content. Some fruits are lower in sugars and thus can be consumed in moderation. The glycemic index of fruits also plays a role, as it measures how much a food item can elevate blood glucose levels. Selecting low-glycemic fruits can help keep blood sugar stable.
Moreover, it's imperative to consider portion sizes. While certain fruits may fit within the keto guidelines, overconsumption can lead to unintentional carbohydrate overload. Keeping track of how much and which fruits are consumed is a simpler yet effective measure for maintaining a ketogenic state. Incorporating fruits mindfully can also lead to improved satiety, as they bring natural fiber and various vitamins.
"The key to success with a ketogenic diet is not to cut out carbohydrates entirely but to manage them wisely, especially in terms of fruit consumption."
Meal Planning Strategies
Meal planning is an essential strategy for effectively incorporating fruits into a ketogenic diet. To start, select a variety of keto-friendly fruits to ensure dietary diversity. Fruits such as blackberries, raspberries, and lemons can be included to provide flavor and health benefits.
A weekly meal plan can be useful. Include fruits intentionally in meals and snacks. Here are some practical tips for meal planning:
- Choose variety: Include different colors of fruits. This provides a broader range of nutrients.
- Plan portions: Measure out recommended serving sizes. A standard serving for berries might be around half a cup, while half an avocado can be another option.
- Track intake: Use an app or food journal. This helps in maintaining carbohydrate limits without much effort.
- Integration: Add fruits to smoothies or salads to enhance overall meals without significant carb addition.
Recipes Utilizing Keto-Friendly Fruits
When it comes to utilizing keto-friendly fruits, creativity can lead to delightful dishes. Here are some recipe ideas that make the most of these fruits:
- Berry Smoothie: Blend a half cup of spinach, half a cup of blackberries, one tablespoon of chia seeds, and unsweetened almond milk.
- Avocado & Lime Salad: Dice half an avocado and mix with lime juice, salt, and some chopped cilantro for a refreshing side dish.
- Lemon-infused Water: Slice a lemon into water to add zest without any excess carbohydrates.
Research on Keto Diet and Fruits
Understanding the intersection of the ketogenic diet and fruit consumption requires evaluating various research studies. This helps to clarify which fruits align with the principles of ketosis and how they impact health. The importance of examining research on keto and fruits lies in its ability to inform diet decisions based on scientific evidence rather than anecdotal claims. It provides insights into how certain fruits can be integrated into a low-carb dietary pattern while still offering valuable nutrients.
The suggested readings also stress the need for awareness around carbohydrate content and the glycemic index. Not all fruits hold equal carbohydrate value, and this variability plays a crucial role in a ketogenic diet. Some studies indicate that fruits with lower carbohydrate levels and minimal impact on blood sugar can support individuals aiming to stay within the desired macronutrient ratios.
In this section, we will delve into the latest studies about fruit consumption within the keto diet. Research findings illuminate the practicalities involved in blending fruit with a ketogenic lifestyle, providing the foundation for healthier decision-making.
Latest Studies
Research surrounding the ketogenic diet has expanded significantly, revealing fascinating insights into how fruits can fit into this low-carb regimen. Studies have shown that certain fruits can be consumed without derailing ketosis, primarily focusing on those with lower net carbohydrate content. For example, research published in various nutrition journals highlights that berries such as raspberries and blackberries have relatively low carbohydrate grams per serving, making them suitable choices for those on a keto diet.
Another notable area of research explores the impact of consumption timing. Investigating when fruits should be consumed, either with meals or separately, has shown that this can influence blood sugar levels. Furthermore, studies indicate that whole fruits tend to have a lower glycemic index compared to fruit juices. This suggests that the fiber content in whole fruits plays a role in mitigating sharp blood sugar spikes.
Nutritional Research
Nutritional research on keto and fruits has also focused on the broader health implications of fruit consumption within a ketogenic framework. Investigations into the micronutrient profiles of keto-friendly fruits reveal that they provide essential vitamins and minerals while fitting within a low-carb intake.
For example, the potassium levels in avocados can help in balancing electrolytes, an important consideration for those adapting to keto. Nutritional studies have also examined the antioxidants present in fruits like berries, which may contribute to overall health and reduce oxidative stress. Thus, these fruits are not just energy sources; they also enhance health through their nutrient density.
Moreover, understanding the role of dietary fiber, particularly in fruits, has been a key focus area. Fiber plays a critical role in digestive health, and studies show that fiber-rich fruits promote a feeling of fullness, which may aid in weight management. This aspect is particularly relevant for individuals adhering to a ketogenic diet, as maintaining satiety while restricting carbohydrates can be challenging.
Research indicates that careful selection of fruits can provide both enjoyment and essential nutrients in a keto diet.
Overall, embracing scientific studies around fruits in a ketogenic context enhances our comprehension of how to effectively navigate dietary choices while reaping health benefits. This knowledge empowers health professionals, nutritionists, and individuals to make informed decisions that align with their health goals.
Finale
The conclusion of this article on keto-friendly fruits is crucial for readers seeking to align their dietary choices with the principles of the ketogenic diet. Understanding how fruits fit within the low-carb paradigm is not simply about listing which fruits to eat; it encompasses a comprehensive awareness of carbohydrate content, glycemic indexes, and their broader nutritional benefits.
Summary of Key Points
Fruits have a spectrum of carbohydrates that can influence a ketogenic diet in varying degrees. Not all fruits are created equal when it comes to keto, and it is essential to consider their role carefully. In summary, the key points include:
- High-Carb Fruits: Many common fruits are rich in sugars and should generally be avoided, including bananas and grapes.
- Keto-Friendly Options: Berries, avocados, olives, and coconuts stand out as suitable choices due to their lower sugar content.
- Nutritional Benefits: Incorporating these fruits can provide valuable micronutrients and antioxidants without significant carbohydrate overload.
- Portion Control: Understanding net carbs helps in strategizing fruit intake without exceeding carbohydrate limits for a ketogenic diet.
- Research Insights: Current studies continue to analyze the implications of fruit consumption within a keto framework.
Final Recommendations
For those adhering to a keto lifestyle, here are several recommendations to optimize fruit consumption:
- Prioritize Low-Carb Fruits: Choose berries for sweetness, and consider adding avocados for healthy fats.
- Read Labels: When considering packaged or processed fruit products, always examine ingredient lists and nutritional information for hidden sugars.
- Incorporate Strategically: Plan meals around keto-friendly fruits, ensuring they complement other food groups while maintaining a low carb count.
- Consult with Professionals: Health professionals can provide tailored advice based on individual dietary needs, ensuring a well-rounded approach to health.





